MacBPM Documentation
MacBPM Manager Manual

BPM Catalogues
Creating BPM Catalogues
New bpm catalogues can be created with the 'New -> Catalogue' command of the File menu.
The content of a bpm catalogue is shown in windows, the "views" of the catalogue. Within
a view, bpm data records are displayed as a list. The underlined column title in the
header of the list determines the data field, which is used to sort the data records of
the list. Each bpm catalogue has got a main view in which all known bpm entries, that
are not filtered out, are displayed. With the 'Find All' button of the 'Find' dialog
box, new views, that only contain entries, which satisfy certain search criteria, can be
opened. On the contrary to the main view, these windows do not represent an own bpm
catalogue, they only show a special selection of data records of the parent bpm
catalogue. Each view, except the main view, has got an unique view number, so that views
can be distinguished. View numbers are displayed in the window title.
BPM Data Records
Normally, bpm data records consist of a music track's bpm rate, artist, title, version
and label. Additionally to this data, you can define the medium and the owner of the
song. At last, it is possible to set a permanent mark for the record. But notice, this
is only a suggestion how to use the different fields of a data record. You can change
the field identifiers as you like (respectively the column titles) by choosing 'Default
Column Titles...' of the System menu (e.g. instead of label names you can store timing
information). To preserve compatibility between MacBPM documents, it's suggested always
to use the bpm, artist and title fields for the intended information.
A new data record can be added to a bpm catalogue by selecting the 'New Entry' menu item
of the Catalogue menu. In the 'New Entry' dialog box you can enter the required
information for a song. You can use the 'Count BPM' button (the button with the clock),
or alternatively the F14-key, to open the bpm counter described in the chapter "MacBPM
Counter". After bpms have been determined, they can be automatically inserted into the
bpm field of the 'New Entry' dialog box by pressing the OK button of the counter. If
bpms should not be truncated to integers, the 'Truncate BPM values' checkbox of the
preferences dialog box must not be checked.
To enter quickly data in the fifth data field, with the default title 'label', there is
a popup menu with often used input strings. Items can be added, changed or deleted
within this menu, by pushing the corresponding button in the preferences dialog box.
Alternatively, you can add new items by selecting "Add this" in the popup menu. Items
can be removed by selecting the item to delete and pressing 'shift' while releasing the
mouse button.
An entry of a bpm catalogue can be edited if the entry is selected in a view of the
catalogue and the 'Edit Entry...' item of the Catalogue menu is chosen. It is also
possible to double-click a bpm data record.
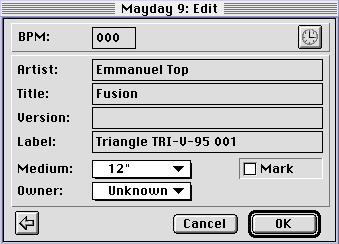
Media And Owners
Media and owners of songs can only be defined, if the appropriate media and owners are
known to the system. They can be declared by using the 'Owner Set...' and 'Medium
Set...' commands of the System menu. After choosing one of these menu items, you can
edit the present owner or medium list.
You can also define a set of default owners and media in the preferences. These default
lists are used to initialize the medium and owner list at MacBPM's startup.
Remember that it's possible to rename the owner and medium fields of a bpm catalogue so
that this data fields can be used to store other information.
Filters
MacBPM provides an import and an export filter for a bpm catalogue. Only entries that
are not filtered out are displayed in the views of the catalogue. The filters are turned
on if the 'Use Filters' menu item is checked.
A filter definition consists of a bpm range and substrings for artist, title, version
and label. Optionally it is possible to declare a medium, an owner and a mark.
An entry matches to a filter if the bpm rate of the entry lies between the lower and the
upper bound of the filter's bpm range, if the substrings of the filter can be found in
the corresponding strings (artist, title, version and label) of the entry and if the
optional values of the filter are equal to the entry's values.
Searching For Data Records
By choosing the 'Find -> Entry...' menu item of the System menu, MacBPM Manager will
present the 'Find' dialog box. A search pattern, which specifies the criteria that are
used to find certain entries, can now be declared the same way as a filter is declared.
If the 'Find' button is clicked, the first entry of the last view, that matches the
search pattern, is highlighted. The last view is the window, that was active before the
'Find' dialog box became the front window. The next entry that matches the search
pattern can now be found by selecting the 'Find Again' command of the System menu.
If the 'Find All' button of the 'Find' dialog box was pressed, a new view is opened and
all entries that satisfy the search criteria are displayed in this new view.
MacBPM Manager supports multi-file search. Select the corresponding checkbox in the
'Find' dialog box to activate multi-file search. The search path is displayed beneath
this checkbox. The 'Options' dialog box for the 'Find' dialog offers the possibility to
change the file path. You are also able to enable or disable the search in nested
folders. There are two different modes for the 'Find All' command, if multi-file search
is turned on:
- List Files:
Searches all files and displays only those names of files, that contain a
matching entry.
If you want the complete pathnames to be shown, select the 'Show full
pathnames'
checkbox of the preferences dialog box.
Double-click a filename of the search result list to open the document.
- Collect Entries:
Searches all files and copies all matching entries to a new bpm catalogue.
The 'Options' dialog box also lets you define the way in which pattern strings are
compared to data fields of an entry. Depending on your settings, a data field matches a
pattern, if the pattern is a substring, a prefix, a postfix or is equal to the data
field.
But remember, the easiest and fastest way to find entries in the frontmost bpm catalogue
is to type in the first few characters of the data field that is used to sort the bpm
catalogue. MacBPM Manager will then show the first entry that matches the input.
Configuring BPM Catalogues
The catalogue name and an additional comment for the catalogue can be entered in the
'Information' dialog box (choose the 'Information...' item of the Catalogue menu and
MacBPM Manager will bring up the 'Information' dialog box). If the checkbox 'Catalogue
names = filenames' of the preferences is checked, the catalogue name is always set to
the corresponding file name.
If you select the 'Save in desktop file' checkbox, MacBPM will store the comment in the
desktop file. After opening the file information dialog box within the Finder (select
'Information' in the Finder's File menu) your comment will then always be displayed.
MacBPM Manager allows the definition of an entry preset. This is a default pattern for
new bpm data records. The fields of the 'New Entry'-dialog are always initialized to the
values of the entry preset.
To change the aligment of columns in catalogue views, or to hide some columns, the
'Column' dialog box has to be used. The settings that are made here, only concern the
parent window. They are also used if this window is printed.
To change the width of a column, click the corresponding border line in the header of
the table (the line in which the column titles are displayed) and drag this line to the
desired position.
Input/Output Of BPM Catalogues
Normally, bpm catalogues are saved in an own format. It is also possible to save a
catalogue as a text file, so that catalogues can be exchanged with database programs.
In text files, the fields of data records are seperated by TABs and records are
seperated by carriage returns (ascii-code 13). MacBPM assumes that only those fields of
a data record are exchanged, that are selected within the 'Text Im-/Export' dialog (that
applies to text import and export). Nethertheless, the order of the data fields within a
text-data record needs to be equal to the order of the columns within the program. If
there is another order in a text file, it may be possible to re-arrange the column order
with MacBPM's tool 'Exchange columns' (but remember, this is only possible with columns
that are compatible to each other).
If a text file is imported in MacBPM Manager, make sure, that either all media and
owners are known, or that the checkboxes 'Accept new media' and 'Accept new owners' of
the preferences are checked. Otherwise MacBPM Manager will ignore new media and owners.
Remember, the maximum number of owners and media is currently restricted to 127
different entries.
If some bpms of a text file are floating point numbers, and MacBPM Manager should not
convert them to integers, it is also necessary, that the 'Truncate BPM values' checkbox
is not checked.
Printing Views Of A BPM Catalogue
To print the contents of the frontmost catalogue view, choose 'Print...' from the 'File'
menu. MacBPM Manager will present the standard Print-dialog for your printer.
The File menu also has got a 'Page Setup...' and a 'Print Options...' command, that let
you customize the print characteristics, like font, font size, page numbering and other
options.
Playlists
Creating Playlists
New playlists can be created with the 'New -> Playlist' command of the File menu.
Playlists are sequences of bpm entries. The entries are numbered automatically by MacBPM
Manager, beginning with entry number one. It is possible to add comment lines to the
list so that further information can also be stored within a playlist. There are two
kinds of comments: free comments and comments bound to a bpm data record (called local
comments). If a record has got local comments, there is a small arrow right beside the
entry number. Clicking on this arrow makes the local comments invisible or visible.
Alternatively you can select the 'Fold' menu item of the Playlist menu. The 'Fold
All'/'Unfold All' commands of the Playlist menu let you hide/show the local comments of
all entries.
Compiling Playlists
The 'New -> Entry' command of the Playlist menu inserts a new entry into the playlist.
If a line is selected, this new entry is inserted before the selected line, otherwise it
is appended to the end of the document. After inserting the new entry, MacBPM Manager
will present the standard 'New Entry' dialog box.
Free comments are inserted similarly. To put a local comment to an existing entry, the
entry has to be selected and the 'Add Comment' command has to be chosen. The new global
comment is then inserted as the last global comment of the selected entry. If there is
already a local comment (that is visible) you can also use the 'New -> Comment' command
after selecting this comment, to insert another local comment before the existing one.
Of course, the final arrangement of comments and entries can be done via drag & drop.
Searching In Playlists
Searching for entries in playlists is done like searching for entries in bpm catalogues.
To find a certain comment in a playlist choose 'Find -> Comment...' of the System menu
to bring the 'Find Comment' dialog box to the front. Now you can enter a search pattern
string and a match modus (contains, is, starts with, ends with).
Set the 'Multi-File Search' checkbox if you want to search in all MacBPM documents of a
specified folder.
Miscellaneous Hints
If something is pasted into a playlist, it is inserted before the first selected line.
If there is no selection, it is appended to the former playlist.
The following format is used to exchange text data with MacBPM playlists (EBNF Syntax):
PLAYLIST ::= { LINE }
LINE ::= FREE_COMMENT | GROUP
GROUP ::= ENTRY { LOCAL_COMMENT }
FREE_COMMENT ::= "-" STRING
LOCAL_COMMENT::= "+" STRING
ENTRY ::= [BPM] [ARTIST] [TITLE] [VERSION] [LABEL]
[MEDIUM] [OWNER] [MARK]
Comments and entries are terminated with carriage returns and the data fields of a data
record are seperated by TABs. To declare which data fields are given within a text, open
the 'Text Im-/Export' dialog box and choose the desired columns.
All other playlist features correspond to the descriptions in the bpm catalogue chapter.
Tools
For both, catalogues and playlists, there is a set of tool functions available. These
tools allow modifications of the entries of the frontmost document. The operation is
either applied to all entries of the document or only to the selected ones. At the
moment, the following utilities are available:
- Change Case: The content of the selected column is changed, so that
all characters are upper-case, lower-case or that all
words are capitalized (this means, that the first cha-
racter of all words is set to an upper-case character)
- Change Entries: The owner, medium and/or mark of all entries is set
to a special value.
- Exchange Columns: The content of two (compatible) columns is ex-
changed. This function is usefull, if two do-
cuments with different use of columns should be
unified.
- Remove Marks: All marks are removed.
- Use Documents Titles: Sets the column identifiers to the ones,
that have been saved with the document. This
is only necessary if you open a document of
someone who has got other column titles than
you.
Miscellaneous
If the 'Offscreen Drawing' checkbox of the preferences dialog is checked, MacBPM will
use offscreen graphics for each catalogue view that is opened after the checkbox has
been selected. Offscreen drawing needs more memory but hasn't got the problems that
direct output has with floating windows and screen borders.
Here's a short description of menu commands, that have not been mentioned before.
The 'BPM Counter...' command of the System menu (you can press the F14-key instead)
opens the standard BPM counter, described in the MacBPM Counter section. The timing
method that is used, can be determined by radio-buttons within the preferences dialog.
'Edit Entry...' of the Database menu opens an Edit-dialog for each highlighted bpm
entry. Currently 'Edit Entry...' only opens a maximum of eight dialogs at the same call
of 'Edit Entry...', but generally you are free to have as many Edit-dialogs open, as you
like. The 'Edit...' command of the Playlist menu works the same way.
There are several usefull keyboard shortcuts:
F14 brings the BPM Counter to front
Return opens an Edit-dialog for the selected bpm data records
Ins/Help opens a 'New Entry' dialog box for a new data record
Shift+Ins opens a 'New Entry' dialog box and brings the bpm counter
to the front (you can start to count bpms at once)
Option+Ins opens a 'New Comment' dialog box
Del deletes all selected data records, after the user
confirmed the action
Backspace deletes all selected data records, after the user
confirmed the action
Shift+Del deletes the selected records without asking the user for
confirmation
Crs-Up/Down scrolls one line up or down
PageUp/Down scrolls one page up or down
Enter alternatively to the OK button of the BPM Counter,
you can use the key
MacBPM Manager supports drag & drop. After selecting bpm entries or comments (in
playlists) and moving them to another window (or to another place within the same
playlist), MacBPM Manager will insert the selected contents in the other window if the
mouse button has been released. If the shift key is pressed while releasing the mouse
button, the data will not be copied but moved to the other window.
To duplicate entries and comments within a playlist, simply select the desired lines,
drag them to the right position and press the option key while releasing the mouse
button. The selected lines will not be moved but copied.
Pressing the command key while dragging comments, forces MacBPM to store these comments
as local comments to the entry where the mouse button has been released.
MacBPM Manager supports stationery documents, that can be used as patterns for other
catalogues or playlists. To save a document as a stationery document, simply select the
appropriate menu item of the Format popup-menu within the 'Save As' dialog box.


